The disposition process is a stage in QC processes that ensures product quality and compliance by preventing defective or nonconforming products from reaching customers. Additionally, the disposition sorting and routing process reduces errors and costs by determining whether defective items can be reworked, repaired, or used as-is, minimizing unnecessary scrapping and financial losses. By streamlining decision-making, the disposition process enhances efficiency in manufacturing and the supply chain, preventing production delays and ensuring defects are addressed promptly.
What Is Involved in the Disposition Process
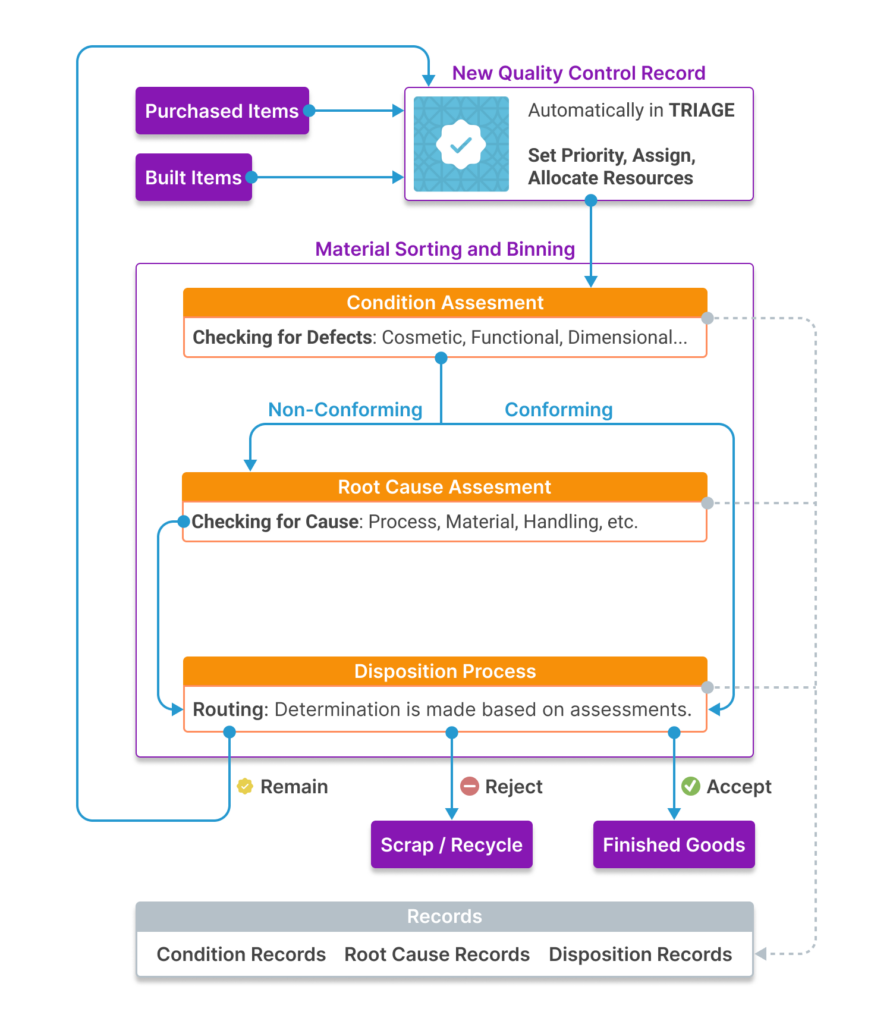
The disposition process in quality control follows a structured approach to handling nonconforming products or materials. It ensures that defects are properly assessed and addressed while maintaining compliance with quality standards. The process generally includes the following steps:
1. Identification of Nonconformance
- A defect, deviation, or issue is detected during inspection, testing, or production.
- The issue is documented in a Nonconformance Report (NCR) or a similar system.
2. Evaluation and Investigation
- The affected product/material is analyzed to determine the cause and severity of the nonconformance.
- Cross-functional teams (e.g., quality control, engineering, production) assess the potential impact on functionality, safety, and compliance.
3. Determining Disposition
- A decision is made on how to handle the nonconforming item. The main options include:
- Use As-Is (UAI): The product is deemed acceptable despite the deviation because the defect does not impact functionality, safety, or compliance.
- Rework: The nonconforming item is modified or repaired to meet quality standards before being released.
- Return to Supplier: The defective material or product is sent back to the supplier for replacement, correction, or credit.
- Scrap: The item is deemed unusable and is discarded to prevent its use in production or sale.
- Concession or Deviation Approval: A temporary approval is granted for the use of nonconforming material under controlled conditions (e.g., for a specific customer requirement).
- Downgrade or Alternative Use: The product is repurposed for an alternate use where the defect does not impact performance.
4. Implementation of the Disposition
- The selected action is carried out (e.g., rework, scrapping, or supplier return).
- Proper documentation is maintained to track decisions and ensure compliance.
5. Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) (If Necessary)
- If the issue is recurring or critical, a root cause analysis is conducted.
- Corrective actions are implemented to prevent future occurrences (e.g., process improvements, supplier quality audits).
6. Final Verification and Closure
- The disposition action is reviewed to confirm that the nonconformance has been effectively resolved.
- The record is closed, and lessons learned may be integrated into process improvements.
This structured approach helps organizations minimize waste, improve efficiency, and maintain product quality and compliance with regulatory and customer standards.
Organizations can track several key metrics from the disposition process to enhance quality control, optimize supplier performance, and improve overall efficiency. These metrics provide insights into the frequency, causes, and impact of non-conformances, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement.
Benefits of Establishing a Standardized Disposition Process
The disposition process plays a critical role in separating non-conforming components from the production line to reduce the risk of their unintended use in finished goods. When defects or deviations from specifications are identified, the process ensures that these components are properly evaluated and classified, preventing their incorporation into final products. This is essential for maintaining quality, safety, and compliance with industry standards.
Once a defect is detected, whether during incoming inspection, in-process quality checks, or final product testing, the non-conforming component is immediately quarantined or labeled to prevent accidental use. This can involve physical segregation in a designated Non-Conforming Materials Area (NCMA) or digital tracking to prevent unauthorized use.
When non-conforming components originate from a supplier, the disposition process provides a structured pathway for Return Material Authorization (RMA) to vendors. The evaluation team determines whether the defect is due to a supplier-related issue, such as incorrect specifications, poor material quality, or manufacturing errors. If the issue is supplier-related, the component is tagged for return, and an RMA request is initiated with the vendor.
Key Disposition Metrics & Their Benefits
Tracking disposition process metrics helps organizations to maintain high-quality standards, reduce waste, and optimize overall efficiency. These metrics provide valuable insights into how non-conforming materials are identified, handled, and resolved, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions that improve production processes and supplier management. Below are several examples of metrics that can be measured from the disposition process.
- Non-Conformance Rate (NCR Rate)
- Definition: Percentage of materials or products that fail to meet quality standards.
- How It Helps: Identifies quality trends, enabling proactive measures to reduce defects.
- Disposition Breakdown by Category
- Definition: Percentage of dispositions (e.g., use-as-is, rework, scrap, return to vendor).
- How It Helps: Provides insights into how non-conformances are handled and highlights inefficiencies in the process.
- Rework Rate
- Definition: Percentage of defective products that require rework.
- How It Helps: High rework rates indicate process inefficiencies, increasing labor and material costs.
- Scrap Rate
- Definition: Percentage of non-conforming materials that are discarded.
- How It Helps: Helps identify excessive waste and opportunities for cost savings.
- Return Material Authorization (RMA) Rate
- Definition: Percentage of non-conforming parts returned to suppliers.
- How It Helps: Measures supplier quality performance and helps in negotiating improvements or replacements.
- Supplier Defect Rate
- Definition: Percentage of incoming materials rejected due to supplier-related defects.
- How It Helps: Helps organizations assess supplier reliability and make informed sourcing decisions.
- Cycle Time for Disposition Decisions
- Definition: Average time taken to identify, evaluate, and take action on non-conforming materials.
- How It Helps: Reducing cycle time minimizes production delays and improves operational efficiency.
- Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)
- Definition: Total costs associated with defects, including rework, scrap, and warranty claims.
- How It Helps: Helps justify investments in quality improvement initiatives.
- Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) Effectiveness
- Definition: Percentage of CAPA actions successfully preventing recurrence of defects.
- How It Helps: Measures the impact of process improvements on reducing non-conformances.
How These Metrics Improve Organizational Effectiveness
By analyzing trends in defects, rework, scrap, and supplier-related issues, companies can proactively reduce costs, minimize production delays, and enhance customer satisfaction. Additionally, monitoring these key indicators helps organizations implement continuous process improvements, ensuring long-term quality and operational excellence. Below is a list of methods and areas where properly analyzing these metrics can make an impact for an organization.
- Data-driven decision-making: Enables proactive quality management by identifying trends in defects and supplier issues.
- Cost reduction: Helps minimize waste, rework, and warranty costs by improving defect management.
- Supplier performance improvement: Allows better supplier selection and accountability based on defect rates and RMAs.
- Faster resolution times: Reduces production delays and enhances operational efficiency.
- Continuous process improvement: Supports ongoing enhancements in quality control and manufacturing processes.
Bringing It All Together
Overall, the disposition process is essential for maintaining efficiency, reducing costs, and improving product quality in manufacturing and supply chains. It provides this benefit through a standardized process that ensures parts are routed efficiently but provides data that can be used to further improve many processes across the organization.
By tracking and analyzing these disposition process metrics, organizations can make strategic improvements that enhance product quality, reduce costs, and optimize supplier relationships, ultimately leading to greater customer satisfaction and business success.
In order to see these benefits from standardized processes and metrics an organization needs to have the right systems in place to collect data and manage the process. A robust quality control system like the one found in Aligni MRP is the best way to go. Sign up today!
Start your 30-day free trial
Join over 4,000 teams that are managing their manufacturing with Aligni.

