All manufacturers perform some sort of production planning. Sometimes it’s just a first in, first out serial process, or it can be a complex system that engages not only production capacity and sales needs but a highly integrated supply chain working together with staged production operations that make sure downtime is minimized without jeopardizing throughput. While the former may be easily done in email and spreadsheets, the latter’s complexity requires specialized systems to oversee efficiently.
Production Planning Defined
Manufacturing production planning refers to the systematic process of creating a detailed roadmap for producing goods efficiently and effectively within a manufacturing facility. It involves a series of strategic decisions and activities aimed at coordinating various resources, processes, and timelines to meet customer demand. It also works to optimize available resources and minimize costs. The primary goal of production planning is to ensure that the right products are produced in the right quantities, at the right time, and with the right quality.
During the production planning process, various factors are considered. These include customer orders, sales forecasts, inventory levels, production capacity, lead times, and resource availability. Those factors are integrated to develop a production schedule that outlines when and how much to produce, as well as the sequence of production activities. This schedule guides the allocation of resources, such as labor, machines, and raw materials, to specific tasks. The schedule is designed to ensure the production process is streamlined and well-coordinated.
Effective production planning contributes to minimizing production downtime, reducing excess inventory, optimizing resource utilization, and ultimately delivering products that meet customer expectations while maximizing operational efficiency.
The steps in the production planning process for manufacturers
To execute production planning well, there are a number of steps a company needs to perform. The specific steps may vary depending on the type of manufacturing, the complexity of the production process, and the tools used, but the following is a general outline of the typical steps manufacturers go through for production planning:
1. Demand Forecasting
The first step in production planning is forecasting the demand for the products. Manufacturers work with the sales department to analyze historical sales data, market trends, customer orders, and other relevant factors to estimate future demand accurately.
2. Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP)
Manufacturers often conduct Sales and Operations Planning meetings to align sales forecasts with production capabilities. These meetings involve cross-functional teams from sales, marketing, production, and other departments to ensure that production plans are in line with sales forecasts and overall business objectives.
3. Capacity Planning
Manufacturers perform capacity planning to ensure that production can meet the demand outlined in the MPS. Capacity planning involves evaluating available production resources, such as labor, machines, and facilities, to identify any potential constraints or bottlenecks.
4. Master Production Schedule (MPS) Creation
Based on the demand forecast and S&OP inputs, the manufacturer creates a Master Production Schedule (MPS). The MPS is a detailed plan that specifies what and how much to produce, considering customer demand, inventory levels, and production capacity constraints.
5. Bill of Materials (BOM) Analysis
The manufacturer reviews the Bill of Materials (BOM) for each product to identify all the components, raw materials, and resources required for production. The BOM serves as a foundation for determining material requirements and production sequences.
6. Evaluating Inventory On-hand
Manufacturers assess the current inventory levels of all materials and components needed for production. This evaluation includes both on-hand quantities and scheduled receipts from suppliers.
7. Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
Using the MPS and BOM information, manufacturers run calculations within a Material Requirements Planning (MRP) system, like Aligni MRP. The MRP system helps determine the quantities and timing of materials and components needed to meet the production schedule while considering inventory levels and lead times.
8. Production Order Release
Once the production plan is finalized, the manufacturer releases production orders based on the scheduled quantities and timing. These orders initiate the actual production process.
9. Execution and Monitoring
Throughout the production process, manufacturers monitor actual production progress, inventory levels, and resource utilization. They may use Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Material Resource Planning (MRP) system, or other monitoring tools to track the status of production orders and ensure that production is proceeding according to plan.
10. Continuous Improvement
Manufacturers continually review and improve their production planning processes based on actual performance, feedback, and changing market conditions. Regularly updating the demand forecasts, inventory on-hand, and refining production plans help ensure that the manufacturing process remains agile and responsive to dynamic market demands.
Why do production planning with MRP systems instead of spreadsheets?
It takes the right tools to get the most out of a production operation. While it’s common for manufacturers to start out trying to plan their production operations within spreadsheets, eventually these homegrown systems won’t keep up with the demands of the company. Still, it may be difficult to see when to transition to a purpose-built system like a Material Requirements Planning (MRP) system without understanding the benefits to be had from the migration.
Using an MRP system, like Aligni MRP for production planning offers several advantages over relying solely on spreadsheets. These systems are specifically designed to handle the complexities of production planning by providing the necessary calculations, data integration, and resource management. Unlike spreadsheets, MRP systems provide a centralized platform where data from various departments, such as sales, inventory, and procurement, can be seamlessly integrated, ensuring accuracy and real-time updates. This eliminates the risk of manual errors that can occur when managing data across multiple spreadsheets.
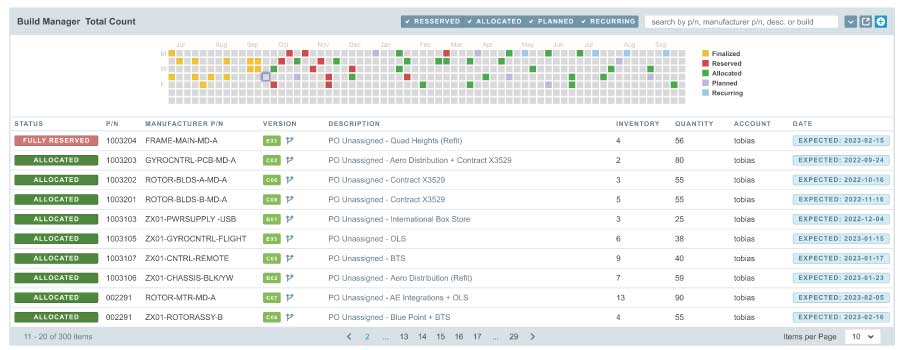
MRP systems are built on the advanced algorithms necessary to optimize material requirements. These systems consider factors like lead times, safety stock levels, and production capacity constraints, resulting in more informed and efficient production plans. Being built upon an item master database instead of two-dimensional tables, MRP systems are far more adept at making a company’s historical data work for them without investing in the time and complexity a competing spreadsheet-based system would require.
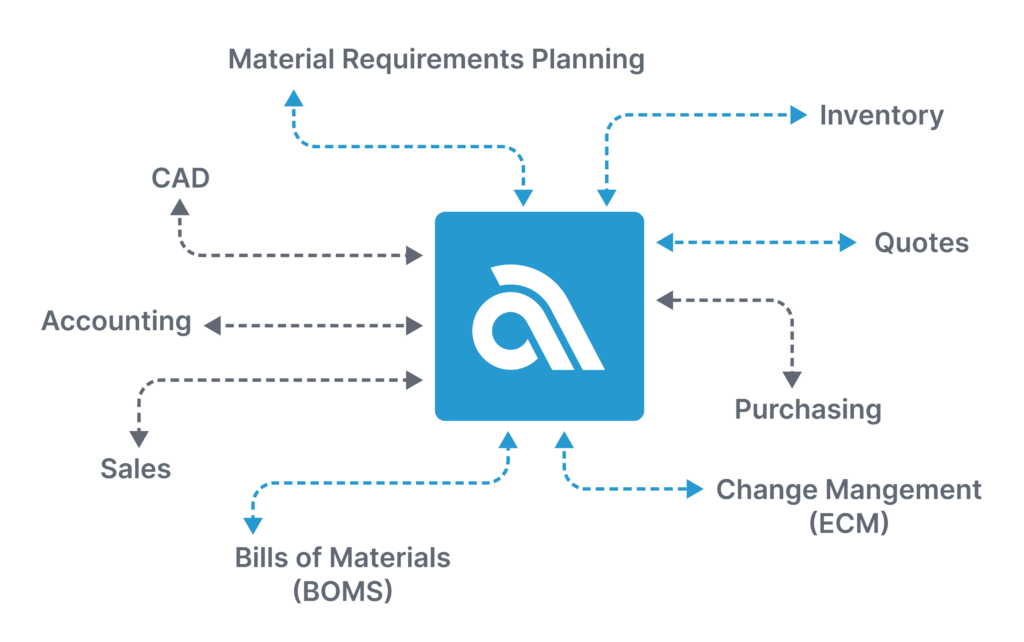
Manufacturers also get enhanced visibility and traceability throughout the production process when using MRP systems. While spreadsheets can quickly become cumbersome and difficult to manage as the complexity of production increases, MRP systems provide a structured framework to track and monitor each stage of production – another feature of the MRP database foundation. This leads to better decision-making and quicker problem resolution. Additionally, MRP systems provide the ability to simulate different scenarios and analyze the potential impact of changes in demand, lead times, or production schedules. This level of scenario analysis is challenging to achieve with spreadsheets alone.
Bringing it all together
Overall, MRP systems offer greater accuracy, efficiency, and flexibility in production planning, making them a more reliable and sophisticated solution compared to traditional spreadsheets. These features and others are the reasons highly efficient manufacturing facilities tend to run MRP systems.
If production planning is getting too complex for your current systems, it’s time to make the change to an MRP system. Sign up for Aligni MRP today.
Start your 30-day free trial
Helping You Make Great Things…Better.
